Situs Blog
Blog terbaru
Blog Kategori
Hubungi kami
- Jika Anda memiliki pertanyaan, silahkan hubungi kami, Semua pertanyaan akan dijawab
- Email : David@tmaxcn.com
- Email : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- Tambahkan : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
Hot produk
blog
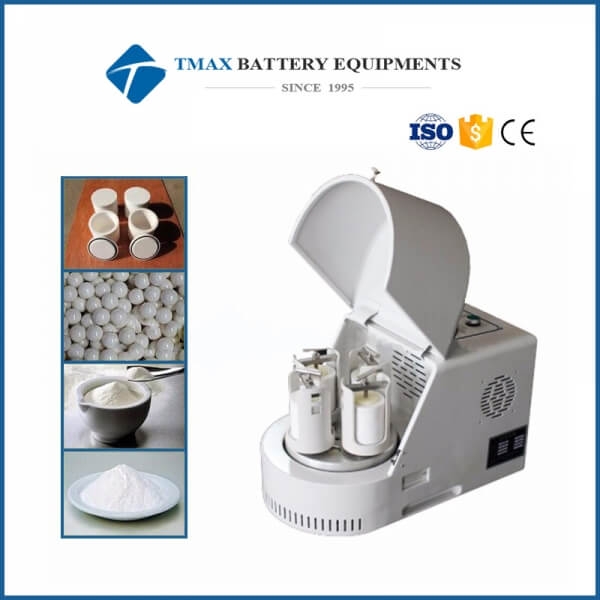
Small Ball Mill
A small ball mill is a compact grinding machine used to reduce materials into fine powders or mixtures. It is widely employed in industries such as mining, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and research laboratories for its ability to process small quantities of materials with precision and efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the principles, design, applications, advantages, challenges, and innovations associated with small ball mills.
●Principles of Operation
1. Mechanism
A small ball mill consists of a cylindrical chamber that rotates around a horizontal axis.
Inside the chamber, grinding media (e.g., steel balls, ceramic balls, or other materials) are added along with the material to be ground.
As the cylinder rotates, the grinding media and material are lifted to a certain height and then fall back down due to gravity, causing collisions and friction that break down the material into finer particles.
2. Key Components
Cylinder: The main body of the mill where the grinding occurs.
Grinding Media: Balls made of materials like steel, ceramic, or glass, depending on the application.
Motor: Drives the rotation of the cylinder at controlled speeds.
Feed System: Adds material into the mill.
Discharge System: Removes the ground material after processing.
●Types of Small Ball Mills
1. BatchType Ball Mills
Operate in batches, meaning the material is loaded, processed, and then discharged before starting another cycle.
Suitable for smallscale operations or laboratory testing.
2. ContinuousType Ball Mills
Allow continuous feeding and discharge of material, making them ideal for largerscale production.
3. Planetary Ball Mills
Use a planetary motion (a combination of rotation and revolution) to achieve higher energy input and finer grinding.
Commonly used in research labs for nanomaterial synthesis.
4. Jar Mills
Smaller in size, often used for laboratory experiments or pilotscale testing.
●Advantages of Small Ball Mills
1. Compact Size
Designed for spacesaving applications, making them suitable for labs and small workshops.
2. Versatility
Can process a wide range of materials, including metals, minerals, ceramics, and chemicals.
3. Precision
Capable of producing fine powders with consistent particle sizes.
4. CostEffectiveness
Lower initial investment compared to largescale industrial mills.
5. Ease of Use
Simple setup and operation, requiring minimal training.
6. Customizable
Available in various sizes and configurations to meet specific needs.
●Challenges in Using Small Ball Mills
1. Material Contamination
If improper grinding media is used, it can contaminate the material being processed.
2. Wear and Tear
The grinding media and mill components may wear out over time, requiring regular maintenance or replacement.
3. Energy Consumption
Although smaller than industrial mills, they still consume significant energy for fine grinding.
4. Noise and Vibration
Operation can generate noise and vibrations, which may require soundproofing or isolation measures.
5. Limited Capacity
Not suitable for largescale production due to their small size.
●Applications of Small Ball Mills
Small ball mills are used across various industries for diverse applications:
1. Mining and Metallurgy
Grinding ores and minerals for analysis or further processing.
2. Ceramics
Producing fine ceramic powders for manufacturing tiles, coatings, and other products.
3. Pharmaceuticals
Mixing and grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
4. Chemicals
Synthesizing and mixing chemical compounds for research or production.
5. Research and Development
Testing new materials, formulations, and processes in laboratory settings.
6. Food Industry
Grinding spices, herbs, and other food additives to desired consistencies.
7. Environmental Science
Preparing soil, water, or waste samples for analysis.
●Innovations in Small Ball Mill Technology
To address challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are developing advanced small ball mill solutions:
1. Smart Monitoring Systems
Incorporating sensors and realtime monitoring to optimize grinding parameters and detect issues early.
2. Advanced Materials
Using wearresistant and corrosionresistant materials for longerlasting components.
3. Automation
Integrating programmable controls for precise and repeatable grinding processes.
4. EcoFriendly Designs
Reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste during operation.
5. Customizable Configurations
Offering tailored solutions for specific materials, particle sizes, and applications.
●The Future of Small Ball Mills
As material processing demands evolve, so too will the technology behind small ball mills. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Precision
Development of ultrafine grinding capabilities for nanomaterials and advanced composites.
2. Focus on Sustainability
Energyefficient designs and ecofriendly materials to minimize environmental impact.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Combining small ball mills with AI, IoT, and cloud computing for smarter diagnostics and analysis.
4. Global Standards Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for material processing.
5. Expansion into New Markets
Adapting small ball mills for emerging fields like biotechnology, aerospace, and quantum computing.
●Conclusion
Small ball mills are an essential tool for material processing, offering versatility, precision, and costeffectiveness for a wide range of applications. Their continuous evolution is crucial for meeting the growing demands of modern industries and research.
February 10,2026.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
A small ball mill is a compact grinding machine used to reduce materials into fine powders or mixtures. It is widely employed in industries such as mining, ceramics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and research laboratories for its ability to process small quantities of materials with precision and efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the principles, design, applications, advantages, challenges, and innovations associated with small ball mills.
●Principles of Operation
1. Mechanism
A small ball mill consists of a cylindrical chamber that rotates around a horizontal axis.
Inside the chamber, grinding media (e.g., steel balls, ceramic balls, or other materials) are added along with the material to be ground.
As the cylinder rotates, the grinding media and material are lifted to a certain height and then fall back down due to gravity, causing collisions and friction that break down the material into finer particles.
2. Key Components
Cylinder: The main body of the mill where the grinding occurs.
Grinding Media: Balls made of materials like steel, ceramic, or glass, depending on the application.
Motor: Drives the rotation of the cylinder at controlled speeds.
Feed System: Adds material into the mill.
Discharge System: Removes the ground material after processing.
●Types of Small Ball Mills
1. BatchType Ball Mills
Operate in batches, meaning the material is loaded, processed, and then discharged before starting another cycle.
Suitable for smallscale operations or laboratory testing.
2. ContinuousType Ball Mills
Allow continuous feeding and discharge of material, making them ideal for largerscale production.
3. Planetary Ball Mills
Use a planetary motion (a combination of rotation and revolution) to achieve higher energy input and finer grinding.
Commonly used in research labs for nanomaterial synthesis.
4. Jar Mills
Smaller in size, often used for laboratory experiments or pilotscale testing.
●Advantages of Small Ball Mills
1. Compact Size
Designed for spacesaving applications, making them suitable for labs and small workshops.
2. Versatility
Can process a wide range of materials, including metals, minerals, ceramics, and chemicals.
3. Precision
Capable of producing fine powders with consistent particle sizes.
4. CostEffectiveness
Lower initial investment compared to largescale industrial mills.
5. Ease of Use
Simple setup and operation, requiring minimal training.
6. Customizable
Available in various sizes and configurations to meet specific needs.
●Challenges in Using Small Ball Mills
1. Material Contamination
If improper grinding media is used, it can contaminate the material being processed.
2. Wear and Tear
The grinding media and mill components may wear out over time, requiring regular maintenance or replacement.
3. Energy Consumption
Although smaller than industrial mills, they still consume significant energy for fine grinding.
4. Noise and Vibration
Operation can generate noise and vibrations, which may require soundproofing or isolation measures.
5. Limited Capacity
Not suitable for largescale production due to their small size.
Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill
●Applications of Small Ball Mills
Small ball mills are used across various industries for diverse applications:
1. Mining and Metallurgy
Grinding ores and minerals for analysis or further processing.
2. Ceramics
Producing fine ceramic powders for manufacturing tiles, coatings, and other products.
3. Pharmaceuticals
Mixing and grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
4. Chemicals
Synthesizing and mixing chemical compounds for research or production.
5. Research and Development
Testing new materials, formulations, and processes in laboratory settings.
6. Food Industry
Grinding spices, herbs, and other food additives to desired consistencies.
7. Environmental Science
Preparing soil, water, or waste samples for analysis.
●Innovations in Small Ball Mill Technology
To address challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are developing advanced small ball mill solutions:
1. Smart Monitoring Systems
Incorporating sensors and realtime monitoring to optimize grinding parameters and detect issues early.
2. Advanced Materials
Using wearresistant and corrosionresistant materials for longerlasting components.
3. Automation
Integrating programmable controls for precise and repeatable grinding processes.
4. EcoFriendly Designs
Reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste during operation.
5. Customizable Configurations
Offering tailored solutions for specific materials, particle sizes, and applications.
●The Future of Small Ball Mills
As material processing demands evolve, so too will the technology behind small ball mills. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Precision
Development of ultrafine grinding capabilities for nanomaterials and advanced composites.
2. Focus on Sustainability
Energyefficient designs and ecofriendly materials to minimize environmental impact.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Combining small ball mills with AI, IoT, and cloud computing for smarter diagnostics and analysis.
4. Global Standards Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for material processing.
5. Expansion into New Markets
Adapting small ball mills for emerging fields like biotechnology, aerospace, and quantum computing.
●Conclusion
Small ball mills are an essential tool for material processing, offering versatility, precision, and costeffectiveness for a wide range of applications. Their continuous evolution is crucial for meeting the growing demands of modern industries and research.
What excites you most about the advancements in small ball mill technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovative tools can shape the future of material processing and product development.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

