Situs Blog
Blog terbaru
Blog Kategori
Hubungi kami
- Jika Anda memiliki pertanyaan, silahkan hubungi kami, Semua pertanyaan akan dijawab
- Email : David@tmaxcn.com
- Email : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- Tambahkan : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
Hot produk
blog
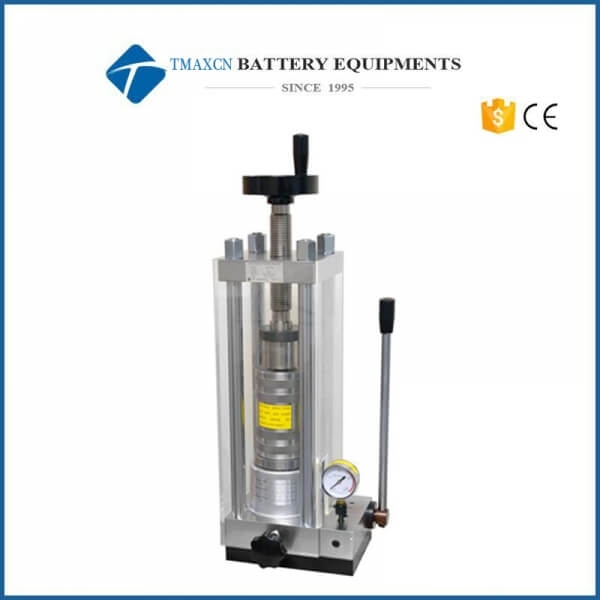
Cold Isostatic Pressing
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a manufacturing technique used to compact powders or other materials into dense, uniform shapes using highpressure fluids. Unlike traditional pressing methods that apply force in one or two directions, CIP uses hydrostatic pressure uniformly in all directions, ensuring consistent density and minimizing defects. This process is widely employed in industries where highperformance components with complex geometries are required.
In this article, we will explore the principles, equipment, advantages, challenges, and applications of cold isostatic pressing.
●Principles of Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Basic Mechanism
The material to be pressed (usually powdered metal, ceramic, or polymer) is placed inside a flexible mold or container.
The mold is then submerged in a liquid medium, typically water or oil, which acts as the pressuretransmitting fluid.
Highpressure pumps generate uniform pressure around the mold, causing the material inside to compact evenly in all directions.
2. Key Parameters
Pressure: Typically ranges from 100 MPa to 400 MPa (approximately 14,500 to 58,000 psi), depending on the material being processed.
Temperature: CIP operates at room temperature, distinguishing it from hot isostatic pressing (HIP), which involves elevated temperatures.
Material Properties: The powder's particle size, shape, and distribution influence compaction behavior and final product quality.
●Equipment Used in Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Pressure Vessel
A robust, sealed chamber designed to withstand extreme pressures during operation.
2. Hydraulic System
Provides the necessary pressure to the fluid medium surrounding the mold.
3. Flexible Mold
Made of materials like rubber, polyurethane, or elastomers, the mold holds the powder and conforms to its shape under pressure.
4. Control System
Monitors and regulates pressure, time, and other parameters to ensure precise control over the process.
●Advantages of Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Uniform Density:
The isotropic pressure ensures consistent density throughout the component, reducing the risk of cracks or voids.
2. Complex Geometries:
CIP can produce parts with intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional pressing methods.
3. High Precision:
Achieves tight dimensional tolerances, minimizing the need for secondary machining operations.
4. Material Versatility:
Suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, composites, and polymers.
5. Scalability:
Can be used for both smallscale prototyping and largescale production.
6. CostEffectiveness:
Reduces material waste and improves yield compared to traditional manufacturing techniques.
●Challenges in Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Initial Investment:
High costs associated with purchasing and maintaining specialized equipment.
2. Mold Durability:
Flexible molds may degrade over time due to repeated exposure to high pressures.
3. Debinding Complexity:
For some materials, removing binders after pressing can be challenging and timeconsuming.
4. Surface Finish:
Parts may require additional finishing steps to achieve smooth surfaces or sharp edges.
5. Size Limitations:
Larger components may require oversized presses, increasing costs and complexity.
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are introducing advanced technologies:
1. Advanced Materials:
Development of durable mold materials and coatings to extend service life.
2. Automated Systems:
Integration of robotics and IoT for improved efficiency and reduced labor costs.
3. RealTime Monitoring:
Sensors and data analytics tools to optimize pressure and time settings during processing.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Improved hydraulic systems and power management to reduce energy consumption.
5. Customizable Solutions:
Modular designs allowing users to adapt equipment for specific applications and materials.
●Applications of Cold Isostatic Pressing
Cold isostatic pressing is widely used across various industries:
1. Aerospace:
Manufacturing turbine blades, engine components, and structural parts with high strengthtoweight ratios.
2. Automotive:
Producing gears, bearings, and other components requiring precise dimensions and uniform properties.
3. Medical Devices:
Fabricating implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments from biocompatible materials.
4. Ceramics:
Creating cutting tools, electrical insulators, and wearresistant components.
5. Tooling and Dies:
Producing molds, dies, and punches with enhanced durability and performance.
6. Nuclear Industry:
Manufacturing fuel pellets and structural components for nuclear reactors.
●The Future of Cold Isostatic Pressing
As technology advances, cold isostatic pressing will continue to evolve to meet the demands of modern manufacturing. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize processing parameters and reduce human intervention.
2. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and energyefficient designs will become standard.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Combining CIP with additive manufacturing, AI, and IoT for smarter and more efficient production processes.
4. Development of New Materials:
Adapting CIP to accommodate advanced materials like nanocomposites and functionally graded materials.
5. Global Standards Compliance:
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for material processing.
●Conclusion
Cold isostatic pressing is a powerful and versatile manufacturing technique that offers unparalleled precision and uniformity in producing highperformance components. Its ability to handle complex geometries and a wide range of materials makes it indispensable in industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices.
December 26,2025.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a manufacturing technique used to compact powders or other materials into dense, uniform shapes using highpressure fluids. Unlike traditional pressing methods that apply force in one or two directions, CIP uses hydrostatic pressure uniformly in all directions, ensuring consistent density and minimizing defects. This process is widely employed in industries where highperformance components with complex geometries are required.
In this article, we will explore the principles, equipment, advantages, challenges, and applications of cold isostatic pressing.
●Principles of Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Basic Mechanism
The material to be pressed (usually powdered metal, ceramic, or polymer) is placed inside a flexible mold or container.
The mold is then submerged in a liquid medium, typically water or oil, which acts as the pressuretransmitting fluid.
Highpressure pumps generate uniform pressure around the mold, causing the material inside to compact evenly in all directions.
2. Key Parameters
Pressure: Typically ranges from 100 MPa to 400 MPa (approximately 14,500 to 58,000 psi), depending on the material being processed.
Temperature: CIP operates at room temperature, distinguishing it from hot isostatic pressing (HIP), which involves elevated temperatures.
Material Properties: The powder's particle size, shape, and distribution influence compaction behavior and final product quality.
●Equipment Used in Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Pressure Vessel
A robust, sealed chamber designed to withstand extreme pressures during operation.
2. Hydraulic System
Provides the necessary pressure to the fluid medium surrounding the mold.
3. Flexible Mold
Made of materials like rubber, polyurethane, or elastomers, the mold holds the powder and conforms to its shape under pressure.
4. Control System
Monitors and regulates pressure, time, and other parameters to ensure precise control over the process.
●Advantages of Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Uniform Density:
The isotropic pressure ensures consistent density throughout the component, reducing the risk of cracks or voids.
2. Complex Geometries:
CIP can produce parts with intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional pressing methods.
3. High Precision:
Achieves tight dimensional tolerances, minimizing the need for secondary machining operations.
4. Material Versatility:
Suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, composites, and polymers.
5. Scalability:
Can be used for both smallscale prototyping and largescale production.
6. CostEffectiveness:
Reduces material waste and improves yield compared to traditional manufacturing techniques.
●Challenges in Cold Isostatic Pressing
1. Initial Investment:
High costs associated with purchasing and maintaining specialized equipment.
2. Mold Durability:
Flexible molds may degrade over time due to repeated exposure to high pressures.
3. Debinding Complexity:
For some materials, removing binders after pressing can be challenging and timeconsuming.
4. Surface Finish:
Parts may require additional finishing steps to achieve smooth surfaces or sharp edges.
5. Size Limitations:
Larger components may require oversized presses, increasing costs and complexity.
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are introducing advanced technologies:
1. Advanced Materials:
Development of durable mold materials and coatings to extend service life.
2. Automated Systems:
Integration of robotics and IoT for improved efficiency and reduced labor costs.
3. RealTime Monitoring:
Sensors and data analytics tools to optimize pressure and time settings during processing.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Improved hydraulic systems and power management to reduce energy consumption.
5. Customizable Solutions:
Modular designs allowing users to adapt equipment for specific applications and materials.
●Applications of Cold Isostatic Pressing
Cold isostatic pressing is widely used across various industries:
1. Aerospace:
Manufacturing turbine blades, engine components, and structural parts with high strengthtoweight ratios.
2. Automotive:
Producing gears, bearings, and other components requiring precise dimensions and uniform properties.
3. Medical Devices:
Fabricating implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments from biocompatible materials.
4. Ceramics:
Creating cutting tools, electrical insulators, and wearresistant components.
5. Tooling and Dies:
Producing molds, dies, and punches with enhanced durability and performance.
6. Nuclear Industry:
Manufacturing fuel pellets and structural components for nuclear reactors.
●The Future of Cold Isostatic Pressing
As technology advances, cold isostatic pressing will continue to evolve to meet the demands of modern manufacturing. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize processing parameters and reduce human intervention.
2. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and energyefficient designs will become standard.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Combining CIP with additive manufacturing, AI, and IoT for smarter and more efficient production processes.
4. Development of New Materials:
Adapting CIP to accommodate advanced materials like nanocomposites and functionally graded materials.
5. Global Standards Compliance:
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for material processing.
●Conclusion
Cold isostatic pressing is a powerful and versatile manufacturing technique that offers unparalleled precision and uniformity in producing highperformance components. Its ability to handle complex geometries and a wide range of materials makes it indispensable in industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices.
What excites you most about the role of cold isostatic pressing in advancing manufacturing technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how this innovative process can shape the future of industrial production.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

